All you need to know about your products!

| 3DNews Vendor Reference English Resource - All you need to know about your products! |
||||||
 |
||||||
|
|
||||||
ECS GF8200A (NVIDIA GeForce 8200) with integrated graphicsAuthor:Date: 03/08/2008
The release of the AMD 780G chipset has become a remarkable event in the IT industry. The speed of its integrated graphic core has proved to be very fast, and the functionality so vast that we had to test four boards to examine the chipset from all the aspects. We also note that this product has immediately turned popular, and all the leading manufacturers have represented at least one motherboard based on the AMD 780G chipset. And what about the major competitor of AMD - NVIDIA? All this time, it has been coping with various technical issues, and the first products on new chipsets have appeared quite recently. Therefore, we are testing a motherboard based on the integrated chipset NVIDIA GeForce 8200. But before that we note that NVIDIA has expanded the assortment of chipsets with the integrated graphics and included hi-end products (e.g., nForce 780a). All that is due to the latest Hybrid SLI technology which includes two important features: GeForce Boost, and HybridPower. The former is an analog to the Hybrid Crossfire and is aimed at value systems. Its idea is simple: if the user installs a value external video card (GeForce 8500 GT or GeForce 8400 GS) and enables the GeForce Boost, the computational resources of the external video card and the integrated video core are consolidated. Thus, the user gets some speed gain in 3D applications. The latter feature (HybridPower) is a tribute to modern fashion for power-saving. Assume that the user has a high-end system with two, three or four video cards merged into an SLI array. That results in an unparalleled high speed in the most advanced games and 3D applications. But once the user quits Crysis and launches a web browser (or solitaire), all these four video cards put quite a high load uselessly (of course, unless there is winter outside) and add to the electricity bills. This situation is fixed by the HybridPower feature which seamlessly disables all the external video cards thus switching the load to the integrated video core. Needless to say, the HybridSLI technology is rather complicated from the viewpoint of developers and programmers, which explains the delay in releasing new chipsets. We now examine the GeForce 8200 chipset (code name - MCP78S) aimed at value systems. To start with, in terms of functionality this chip is not inferior to AMD 780G, it decodes and plays HD video as easily. The graphic component of the core as well has been improved substantially. In particular, there is support for DirectX 10.0, with the speed of running 3D applications has been substantially increased. 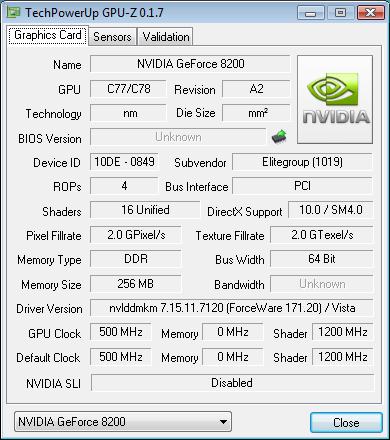
GPU-Z info
What else? The chipset implements support for the PCI Express v2.0 bus and also supports one x16 slot. Since the bandwidth of v2.0 is twice as much as the previous specification, some dodgy engineers can implement two slots having eight lanes each and thus get a SLI system on par with previous high-end chipsets (although these are merely our assumptions). 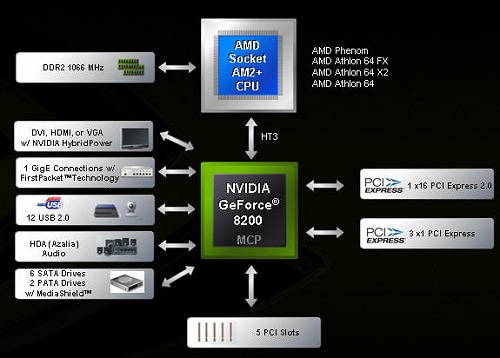 Now on to the expansion options. In this regard, engineers at NVIDIA have gained some progress as compared to the capabilities of nForce 630a. The most essential improvement is about the increase in the number of SerialATA links from four to six. The remaining improvements are minor and (at first glance) unnoticed. Another important point to note: engineers at NVIDIA have merged one powerful and functional graphic core, the new PCI Express v2.0 controller, and the improved south bridge within one chip. Therefore, the heat emission of GeForce 8200 is quite at a high level and according to some rumors the delays with releasing this chipset are caused just by that. Indeed, during the tests the radiator on ECS GF8200A was heating up quite immensely but we did not come up against any issues or operational failures. In conclusion, we bring in a comparative table of specifications for the GeForce 8200 chipset versus the specifications of the previous generation of NVIDIA integrated chipsets.
* - The maximum memory frequency depends on the CPU used. In this review, we also included the motherboard abit A-N68SV (NVIDIA GeForce 7025) to find out the performance boost in the integrated graphic core GeForce 8200. Specifications 
Retail boxes  Package bundle
The package bundles of both the motherboards is almost identical.  Both the boards lack power supply adapters for SerialATA devices. Therefore, the buyer will either have to buy matching adapters or make sure the PSU has the right connectors.   Although the package bundle is too scarce, we don't think it is a shortcoming because that is made up for by the retail price. Layout and FeaturesApart from them chipsets, the major distinction between the boards is in their form factors. In particular, abit A-N68SV is made in the Micro-ATX format, while the ECS board - in the full-fledged ATX.   Engineers at abit have provided only two 240-pin DIMM slots each for DDR2 memory modules, with the overall supported memory capacity being 4 GB. On the contrary, the ECS board uses for slots for DDR2 and therefore the overall memory capacity may be as much as 8 GB.   As we already said, two slots are quite enough for the average value system, however, four slots allow for a more flexible configuration of memory modules and a more optimum use of cheap 512 MB modules. Then, both the motherboards offer the integrated GeForce graphic core and allow for using an external video card which is installed into the PCI Express x16 slot.   The configuration of the remaining ports is as follows: the abit board uses two PCI and one PCI Express x1 slots. The large dimensions of the ECS board allowed the engineers to fit three PCI and two PCI Express x1 slots. We also note that to cool the chipset both the motherboards use only an aluminum radiator. Although the dimensions of the radiator on the ECS board are much larger, the ratings for the cooling system are the same because these boards use different chipsets. The expansion options of the GeForce 8200 chipset are superior to the 7025. In practice, this results in a superiority of the ECS board at the number of SerialATA links. There are six links: five ports are located near the chipset, with one more brought over to the rear panel. On the abit board, all the four ports are positioned near the chipset.   A similar situation is with the number of USB ports. The abit motherboard supports ten USB2.0 ports: four of them are installed on the rear panel, with 6 more ports plugged in with brackets (missing in the package bundle). There are six additional ports on the ECS board (the required brackets are also missing in the package bundle). However, there are six ports on its rear panel (12 altogether), which is more convenient. Both the motherboards implement the Intel High Definition Audio subsystem. On the other hand, the abit board supports six channels (ALC662 chip is used), while the ECS board - eight (IDT 92HD206XX5 chip).   Now a few words on the network support: the abit board uses the RTL8101B chip made by Realtek (10/100 Mbit), and the ECS - RTL8111B (10/100/1000 Mbit) made by the same company:   The board's rear panel is of the following configuration:   We note that the boards lack both COM ports and the one LPT port. On the abit board, they are missing completely, and the ECS board supports only one COM port implemented with a bracket (missing in the bundle). There are also differences in the number of outputs of the integrated graphic core. The abit board uses VGA and DVI, and on the ECS product - a standard VGA and more up-to-date HDMI. Besides, one SerialATA port is brought over to the rear panel of the ECS port. And lastly: since the abit board uses a much cheaper audio subsystem, there are only three audio outputs on the rear panel versus six on the ECS board. Here is a traditional diagram of the boards (we found only a diagram for the abit board):  Of the traits of the product, we note the Power and Reset buttons installed on ECS GF8200A.  Now on to the BIOS settings. BIOSthe BIOS of abit A-N68SV is based on the Award BIOS Phoenix version, while the BIOS of ECS GF8200A - on the AMI BIOS version.   At first glance, the ECS board offers a wider selection of memory frequencies. However, we should keep in mind that the memory frequencies are in direct dependence on the memory controller integrated into the CPU. In the end, the DDR2-1066 MHz frequency is unattainable on principle for our test specimen of the CPU built on the Orleans, and that the respective item in the ECS menu is available is a flaw of the BIOS.   In the respective subsection, the user can set the required memory latency timings, and their number is vast enough in both the boards:   The system monitoring section of the abit board is somehow more powerful than the similar one in the ECS product.   In particular, apart from the temperature of the CPU and the system, the abit board also keeps track of the temperature of the power converter. The abit board also determines a greater number of voltages. Both the boards support the feature for dynamic adjusting the rotational speed of the CPU cooler depending on the CPU temperature.   Besides, the user of the abit board can also keeps track of the monitoring data using the Windows utility FanEQ:  Using the FlashMenu utility, it is possible to update the BIOS firmware:  We note the feature for controlling the memory capacity allocated for the needs of the graphic core:   In conclusion, we note that ECS GF8200A due to the latest chipset supports the Hybrid SLI technology (an analog of the Hybrid Crossfire).  In the forthcoming materials, we'll tell how effective it is. Overclocking and stabilityabit A-N68SV implements a 3-line scheme and uses six 680 mkF and four 1000 mkF capacitors. ECS GF8200A also uses a 3-line scheme but a different kit of capacitors: six 820 mkF and four 270 mkF.   Now on to the overclocking features.  
Now let's look at the practical results of overclocking. To start with, despite the great number of overclocking tools, the ECS board simply wouldn't overclock the test CPU at all. On the other hand, there were no issues with the abit board - overclocking is possible, but the results are below the average.  We produced these results with the earlier versions of the BIOS. Then we updated the BIOS for the abit board with the firmware version 14 and were annoyed by the fact that the feature for multiplier adjustment ceased to work. In fact, it did work, but any value that differs from the nominal (11) was replaced with 10. After that, we updated the BIOS firmware of the ECS board to version of 22 May and were delighted to see that the "M.I.B." section appeared: 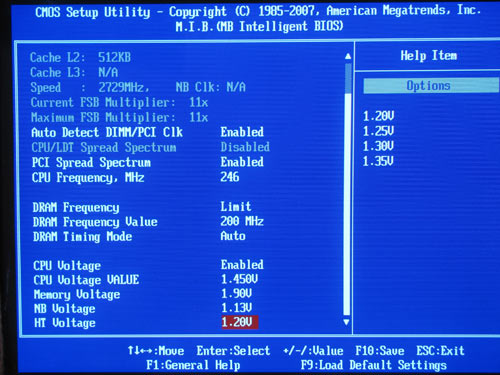 All the overclocking tools remained unchanged (HTT frequency, voltage ranges), and it is convenient that they are all on the same screen. But the nicest thing is that all the features resumed to work and we were able to achieve the HTT=246 MHz. The capability of the board is definitely higher, but you can't measure it without reducing the CPU multiplier (this feature is not supported by ECS GF8200A). We also note the lack of features for overclocking the integrated graphic core. We were especially delighted by the ECS board because we wanted to compare the overclocking efficiency of the GeForce 8200 chipset versus its direct competitor - AMD 780G (in ECS A780GM-A the overclocking tool was implemented). Performance testsIt turned out that while determining the starting FSB speed, the boards set it at a high enough precision.   In our test setup, we used the following hardware:
Let's first take a look at the results of synthetic benchmarks.        Now on to the gaming benchmarks.    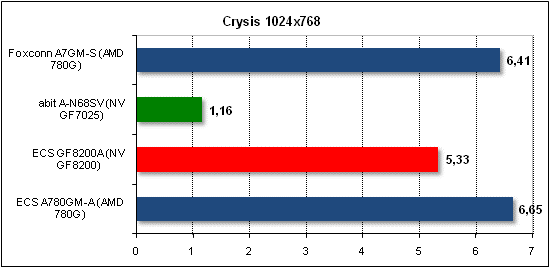     Tests of application software.   
Video encoding (DivX, Xvid) was measured in seconds, i.e. the less the better.
 
Data compression (WinRAR) was measured in KB/sec, i.e. the more, the better.
 In general, the performance of the integrated video core NVIDIA GeForce 8200 is on par with its direct competitor - AMD 780G. Therefore, at this stage we can make a conclusion as to which of these two products are more preferable. Apart from the speed, we should also verify the remaining features and technologies of the GeForce 8200 (e.g., the efficiency of Hybrid SLI). As regards comparison of GeForce 8200 versus the previous generation of NVIDIA's integrated chipsets, we can make only one conclusion: an undisputable victory at both the speed and the functionality. The only 3D application where the GeForce 7025 chipset can oppose against the GeForce 8200 is the game "Company of Heroes". But in reality that is not quite the case, because GeForce 8200 'honestly' displayed image in DirectX 10.0, whereas with 7025 the game enabled the 'lite' mode of rendering (since GeForce 7025 does not support DirectX 10.0). If the mode weren't there, the results would have been the same as in the game "PT Boats". Final WordsFirst, we make conclusions regarding the GeForce 8200 chipset. In our view, it is quite a successful product and motherboards built on its base will be able competing successfully against boards based on AMD 780G. Besides, NVIDIA is planning to release two more modifications: GeForce 8100 and GeForce 8300, which will let the manufacturers to expand the assortment of motherboards substantially. Now conclusions regarding abit A-N68SV and ECS GF8200A. Above all, the boards are within different pricing categories. The abit board cost about $65, whereas the prices for ECS GF8200A are a bit above $86. So, if you are into saving at any rate, the choice is evidently in favor of abit A-N68SV (or another one based on GeForce 7xxx). By the way, the $23 difference today is the difference between dual-core Athlon64 X2 4000+ and Athlon64 X2 5000+. If the $23 is not a critical amount, it's better to choose a board based on GeForce 8200. In particular, buying an ECS GF8200A we get more expansion slots, 8-channel audio (instead of 6-channel), six SerialATA links (instead of four), a Gigabit LAN controller (instead of 10/100 Mbit), twelve USB 2.0 ports (instead of ten), and four slots for memory modules (merely two on the abit board). And of course the user gets a much faster (about 2 times as fast) and functional integrated video core with support for DirectX 10.0, HybridSLI, etc. As regards overclocking, at that we ascertain an provisional equality because of the lack (and incorrect functioning) of the feature for multiplier adjustment.   Conclusion
- Discuss the material in the conference
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||