All you need to know about your products!

| 3DNews Vendor Reference English Resource - All you need to know about your products! |
||||||
 |
||||||
|
|
||||||
Foxconn X38A (Intel X38)Author:Date: 04/12/2007
Today, we are reviewing another motherboard built on the Intel X38 chipset. Release of Intel's new high-end chipset has not proved users' expectations. Yes, it does support sufficient number of PCI Express bus lanes (of the new v2.0 specifications) to make it possible for the developers to install two PCI Express x16 slots with 16 lanes allocated to each. Therefore, two AMD video cards in the Crossfire mode will show the best performance. Besides, some motherboards based on X38 (e.g., Foxconn X38A) offers the third PCI Express x16 slot to which there are four PCI-E bus lanes are allocated. You can install a third video card or a physics accelerator (although the fashion for such devices has already passed).  There are no other advantages in X38. Support for the PCI Express v2.0 bus does not give a real speed gain, and the expansion options remained at a level similar to that on P35-based motherboards . The latter is no wonder, because both the motherboards use the same south bridge ICH9 (R). Finally, Intel has deferred introduction of the 400 MHz (1600 QPB) system bus to 2008, and officially the bus is not supported by X38. Somehow or other, the X38 is the most advanced product in Intel's assortment, and partners of this manufacturer have started production of motherboards. Foxconn is among the first companies which presented its X38A model which stands out with its three PCI Express x16 slots and quite powerful expansion options. Besides, among the board's features is support for both DDR2 and DDR3! Foxconn X38A specifications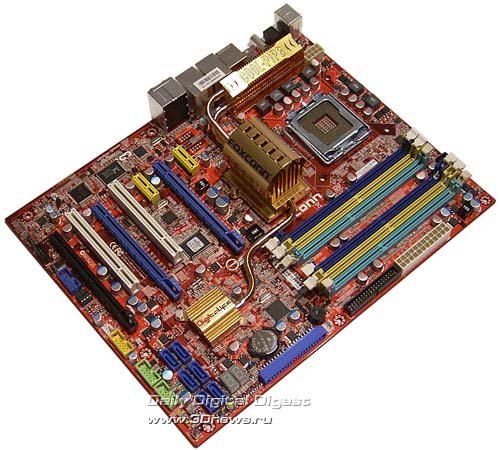
PackageThe motherboard Foxconn X38A is packaged inside an impressive box:  One page tips up, and the user can get a brief idea of all Foxconn's proprietary technologies, as well as watch the board through transparent windows.  The board itself is inside a transparent protective bop of soft plastic.  Package bundle:
The board's package bundle looks balanced enough. In particular, there is a great number of SerialATA cables with the required power adapters, PATA and FDD cables,  as well as one bracket for two additional USB 2.0 and Firewire ports.  Interestingly, to use all the USB ports it is required to buy merely one bracket for two ports. The thing is, Foxconn X38A supports only eight USB 2.0 and not twelve ports like all the other boards with the ICH9R south bridge. Besides, we note the lack of a bracket for a COM port. We had no claims as to the documentation: the main user's guide unveils all the stages of system assemblage and setup. And the brief guide is a good addition to the main guide.  Nor there is anything to complain about the CD which, along with the required drivers and Foxconn's proprietary utilities offers third-party software: Norton Internet Security 2006. Foxconn X38A: Layout and FeaturesThe board's design offers a few interesting traits. First, X38A uses three PCI Express x16 slots. And the developers have managed to avoid blocking of DIMM slots by the first PCI Express video card.  By the way, there are six memory slots on board, which also hasn't made the lives of engineers at Foxconn easier. As regards the power supply connectors, there are all positioned in a really convenient way - the main 24-pin on the bottom end of the board, with the additional 8-pin in the upper right-hand corner of the board. We should also note here that the board operates on plugging in to the PSU of the old configuration of cables (in particular, 20+4). Near the CPU socket, there is a 4-pin CPU_FAN connector for a matching cooler.  But it is installed in quite an inconvenient point - near the north bridge, and access to the connector is hindered by the video card and heat pipes running from the chipset's radiator to the radiator on the power supply module.  Besides the CPU_FAN, there are two more 3-pin connectors onboard: FAN1 - near the north bridge, FAN3 - near the DIMM slots, as well as the 4-pin SYS_FAN - on the left-hand edge of the board. Note that to the FAN1 you can plug in an additional fan (available in the bundle) which is mounted on the radiator of the north bridge.  The board offers a passive system for cooling the chipset and a power supply module. On the north and south bridges, as well as on the power components of the power supply module, there are massive radiators; they are all linked with heat pipes. Under the north bridge, there are four 240-pin DIMM slots for DDR2 memory modules. There is also a pair of 240-pin DIMM slots for DDR3 modules; however, you can't use DDR2 and DDR3 at the same time. The slots are partitioned into two groups. The first group relates to the first link of the controller, the second one - to the second.  The overall memory capacity makes 8 GB for DDR2 and 4 GB for DDR3. There are three PCI Express x16 v2.0 slots (all with latches) which are meant for video cards.  Sixteen bus lanes are allocated to the first and second slot, and merely four (because of the chipset's limitations) - to the third (black) slot. Besides the above listed slots, Foxconn X38A uses two more "regular" PCI slots as well as two PCI Express x1 slots. Expansion optionsFoxconn X38A uses the south bridge ICH9R with a radiator. In the end, the board supports six SerialATA II ports (blue connectors) and allows merging hard disks into RAID arrays of levels 0,1,5, and 10 (MatrixRAID).  Besides, two more SerialATA II devices can be plugged in to the JMB363 controller made by JMicron. The same chip provides support for an additional ParallelATA line. 
Additional SATA connectors are brought to the board's rear panel
Therefore, as many as 10 hard disks (8 SATA + 2 PATA) altogether can be plugged in to Foxconn X38A. Then, the board offers merely 8 USB 2.0 ports. Four ports of them are on the rear panel, with 4 more plugged in with brackets (the board comes bundled with 1 bracket for 2 ports). It is not quite clear why engineers at Foxconn have given up implementation of all the twelve ports which support the ICH9R. Perhaps, based on the PCB of X38A one more model on which the "missing" ports will be enabled for other features may be released. Although the PCB itself offers a wiring for additional USB connectors.  Besides, Foxconn X38A supports the IEEE1394 ("Firewire"). For that, there is a Texas Instruments' TSB43AB22A controller onboard.  Therefore, the board offers support for 2 Firewire ports: one located on the rear panel, with another one connected with a bracket (available in the package bundle). Then, Foxconn X38A offers 8-channel integrated Intel High Definition Audio, with an ALC888S chip used as the codec. Note that engineers at Foxconn have implemented the Dual Digital Audio technology which allows outputting two independent audio streams.  A few words on the network support: the board uses two high-speed LAN controllers: first - Realtek RTL8111B (Gigabit Ethernet),  second - RTL8110SC (Gigabit Ethernet), also made by Realtek.  The board's rear panel has the following configuration.  Above all, we first note the lack of LPT- and COM-ports, whereas one COM port is implemented with a bracket (missing in the bundle). On the rear panel, there are four USB 2.0 ports, a Firewire port, two SerialATA ports, as well as an optical and coaxial SPDIF outputs. Here is the traditional layout of the board:  On Foxconn X38A, there is only one CLR_CMOS jumper meant for clearing the CMOS and is positioned near the battery. Of the additional features, we note three buttons on board: power-on and system reset, as well as one to clear the CMOS. Besides, there is a 7-stage POST indicator with which the user can perform an initial diagnostic (but the documentation lacks a description of the codes). Now on to the BIOS settings. BIOSThe BIOS of Foxconn X38A is built on the AMI BIOS version.  The memory settings are pretty scanty:  There is also the parameter in charge of setting memory operating frequency. But it has vanished in the latest BIOS version.  Instead of it, there is a parameter in charge of the memory frequency described in the "Fox Central Control Unit" section:  Now move on to the section to do with the system monitoring.  The board displays the current temperatures for the processor and the system, voltage, as well as rotational speeds of all the three fans. Note that the CPU cooler and the cooler plugged in to the SYS_FAN are able adjusting the rotational speeds depending on the temperature of the CPU and the system.  The board also allows controlling the modern features of the CPU.  Besides, you can trace the system monitoring readings from within Windows as well. For that, there is the system utility Fox One.  With Fox LiveUpdate, the user can update the BIOS version:  Finally, the utility for updating the POST image has been returned. There was time when it was just the Foxconn utility which used to be the best in this field, now the Fox Logo utility is the best, convenient and easiest to use.  Overclocking and stabilityPrior to moving to overclocking, let's look into the power converter. It uses a 6-phase power scheme, in which there are four 271 mkF and nine 561 mkF capacitors.  To facilitate the thermal mode of the power supply module, there is quite a massive radiator on the power components. Now move on to examining the overclocking tools which are gathered in the "Fox Central Control Unit" section.  First off, Foxconn X38A allows adjusting the system bus speed within the nominal (200/266/333) to 800 MHz in 1 MHz increments. Of convenience is that you can enter the desired FSB value from the keyboard. Secondly, the board allows raising the CPU voltage (Vcore) by 0.3875V in 0.0125V increments.  Then, the advanced user can raise the Vmem by 0.892V (in 0.032V increments).  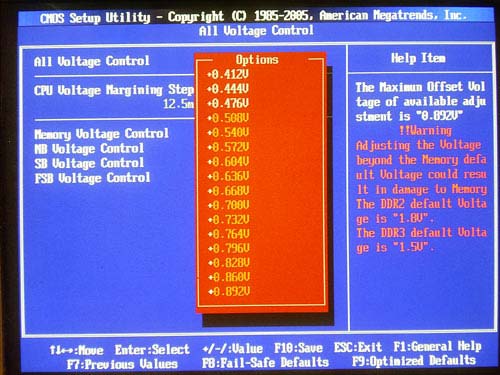 The programmers at Foxconn have implemented a multi-colored highlighting of values. Safe values are highlighted in customary white, with those potentially dangerous highlighted in red-orange. We get a feature for raising voltage on the north bridge (by 0.38V in 0.032V increments)  Besides, the user can raise voltage on the south bridge by 0.424V (in 0.037V increments)  and on the system bus - by 0.56V (in 0.08V increments).  During the overclocking experiments, we came across numerous problems which the board was to blame for. But a couple of days before the review was complete, the new BIOS (723F1P03) was released in which most of the errors were fixed. Nevertheless, the maximum stable FSB speed in the test specimen was 400 MHz.   We are not enumerating the BIOS flaws over here. The thing is, we got one of the preliminary engineering samples, and the final version of the board will arrive at our lab in mid-December (right at the time when the comparative roundup review of motherboards based on P35 and X38 has been published). At that time, we'll also determine the true overclocking capability of Foxconn X38A. Performance testsWhile determining the starting FSB speed, the board overstated it by 0.7 MHz.  In our test setup, we used the following hardware:
We have tested Foxconn X38A with both DDR2 and DDR3 memory. We note it straight that we were unable to set the DDR3-1333 frequency (although officially the board supports that). Quite possibly, because of the BIOS flaws we have a conflict with specific Qimonda modules (although these modules were running absolutely stably at 1400 MHz on the ASUS motherboard):   First, let's look at the results of synthetic tests (other motherboards are based on the following chipsets: Gigabyte X38-DQ6 (DDR2) - on Intel X38, and ASUS Blitz Extreme (DDR3) - on Intel P35).  Now on to the gaming benchmarks.          Final WordsWe attribute all the found flaws to the "raw" state of the engineering sample. However, we note that at the end of the year we'll publish a roundup review of motherboards based on P35 and X38, and we'll come back to testing the Foxconn X38A again. And that will be the final version. We should admit, the flaws were related mostly to the overclocking tools, shortcomings in the BIOS and the software. At all the other parameters, we had nothing to complain about Foxconn X38A. We add that the three PCI Express x16 slots, as well as support for both DDR2 and DDR3 memory makes this product stand out among some other motherboards based on X38. Anyway, we had questions regarding the small number of USB 2.0 ports: why are they only eight? Among the other traits of the board, we should point out the powerful system for cooling the main components, soldered-in buttons, a 7-stage indicator, and a good package bundle. We also liked the LiveUpdate and Logo utilities (the latter one is best in its class).  ConclusionPros:
- Discuss the material in a conference
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||