|
3DNews Vendor Reference English Resource - All you need to know about your products! |
|
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
|
Early in August 2005, there happened inevitable - one of the most successful and long-lived computer platforms, AMD Socket 462 (Socket A), sank into oblivion, officially. It's a pity, but time is implacable - these days, new technologies are increasingly gaining urgency, among which the most significant that determines both the modern look of computers and its immediate future is the PCI Express. From its predecessors it differs in high bandwidth and excellent scaling capabilities. In each channel of the PCI-E bus, data is transmitted in both directions along two pairs of wires (or tracks on the PCB) using the duplex scheme. Today, the theoretical bandwidth of one simplex channel amounts to 2.5 Gbit/s in one direction, or 5 Gbit/s in both. This speed is quite enough for use as the internal system bus. Although today despite the more than a half year of its history, the share of PCI Express chipsets is still insignificant. Nevertheless, they have the future - by the second half of year 2006 the overall number of motherboards for AMD Athlon 64 with support for PCI-Express is expected to exceed that for the boards which support the traditional AGP8X graphic interface. The Athlon 64 family presented in 2003 today has become the major product line of CPUs offered by AMD for desktop computers. They all are based on the extremely successful K8 architecture whose distinguishing features are compatibility to 64-bit extensions AMD64, communication to the "outer world" via the Hyper Transport bus, and, the most important - the memory controller integrated into the processor core. One of the most characteristic (and not the most pleasant) features of AMD platform is the excessive number of processor connector types supported by it. Apart from Socket 940, gradually losing its topicality and which allows using it, together with server processors Opteron, with first models of Athlon 64 FX, actively developing is the Socket 754 platform aimed at building inexpensive computing systems based on Athlon 64/Sempron processors that offer single-channel memory controller, as well as the more "serious" Socket 939 platform for mod-end processor of Athlon 64 class with the dual-channel memory that provide topmost performance. But due to the universality of AMD64 architecture, the variety of design makes of AMD processors brings more problems to consumers rather than to manufacturers - one and the same set of chips may be used for building PCBs with any of the three above listed types of processors. Despite the fact that almost all the modern PCI-E chipsets for AMD platform were announced during 2004, even today motherboards built based on them are a rarity on the shelves of computer shops. Among the exceptions are NVIDIA chipsets of the nForce4 family and, partly, VIA K8T890. NVIDIANot only has NVIDIA nForce4 become the first chipsets for the AMD K8 platform with support for the PCI Express bus on the market of chipsets, it has also proved to be the most functional chipsets among all the known competitors. It's just the functional capabilities that determine the "image" of chipsets for AMD64 - because their memory controller is integrated into the processor, the performance of all modern chipsets is almost the same. It's just the superb "functionality" of nForce4 chipsets that is the cause for their being the base of "top-end" motherboards for Athlon 64 processors on Socket 939. The nForce4 was developed not "from scratch", but is based on the successful enough nForce3 250Gb. Like the predecessor, it is made up of a single MCP chip containing all the peripheral and communication controllers. This scheme of chipset seems to be optimal, since it lacks a memory controller. On the other hand, the relatively large size of the chip (10.5 x 8.1 mm) results in a smaller yield ratio for the chips rather than provides a traditional separate solution with the south and north bridge. The line of NVIDIA nForce4 chipsets is presented with three products. The base version is "simply" dubbed nForce4, the version with advanced functionality - nForce4 Ultra, and finally the intuitive improvement is seen in the "top-end" version - nForce4 SLI. The base version of nForce4 is linked to the processor via a bidirectional 800 MHz Hyper Transport bus (16 bit of bus width in each direction), supports 20 channels of the PCI Express bus (16 of which are enabled in the graphic interface PCI-E x16), two independent SerialATA dual-channel controllers of 150 MB/s bandwidth, which allowed essentially expanding the functional capabilities of tuning and using RAID arrays. In particular, nForce4 offers support for RAID Morphing and Cross-Controller RAID technologies. The RAID Morphing facilitates the tasks of configuring RAID arrays considerably, allowing the user to add new disks into the RAID array "on the fly", as well as change the level of RAID array, e.g. convert an array from RAID 1 into RAID 0. The second feature, as the name suggests (Cross-Controller RAID), allows merging both Serial ATA and Parallel ATA disks into RAID arrays. There is one more interesting feature called Disk Alert. It allows keeping track of correctness of plugging in hard disks and report an error in case a problem comes up. All the main buses of nForce4 are separated, which guarantees a comfortable "overclocking" of the processor (HyperTransport bus) without touching the other buses: PCI Express, SATA, or PCI. Besides, the chipset supports 10 USB2.0 ports (while all the other manufacturers restricted themselves to eight), and an integrated Gigabit LAN controller. The nForce4 Ultra version differs from the base version in the much faster 1000 MHz HyperTransport bus, as well as the Gigabit LAN controller that contains a hardware accelerator for handling network packages (Active Armor), or a software-hardware firewall. The integrated unit for TCP/UDP packages filtration on the hardware level relieves the CPU from doing considerable part of the job filtering the network traffic, and due to its ease of use even for beginners, the software firewall provides system protection against viruses or attacks from the Internet. Besides, the bandwidth of SerialATA controllers has been increased to 300 MB/s. The chipset has been complemented with support for NCQ (Native Command Queuing - optimized execution of queries), as well as the "Hot Swap" feature (for SATA-disks). In fact, nForce4 Ultra has become the first chipset where a full-featured support for SerialATA II has been implemented. In fact, it is very doubtful that such a high speed of SATA II may be in demand in in the foreseeable future, but the new standard will allow using port concentrators that make it possible to plug in two storage devices to each port. The most powerful (and thus the most expensive) modification - nForce4 SLI - provides a simultaneous use of two PCI Express NVIDIA video cards in the SLI mode. The emergence of "two graphic interfaces" in the case of PCI Express is implemented easily enough: the regular PCI-E x16 channel is physically "split" into two slots (of the PCI-E x8 format). In other words, unlike the "basic" and the Ultra versions, the nForce4 SLI chipset is able changing the configuration of PCI Express bus channels. By and large, all the chipsets of the nForce4 line have one more or less evident shortcoming - the integrated 8-channel audio controller meets the already outdated AC'97 standard (support for the High Definition Audio is missing). In the nearest future, the emergence of a new version of NVIDIA's "top-end" chipset - nForce 4 SLI 16x. Its major feature will be support for the functioning of two video cards in the SLI mode, and they both will be able running in the full-featured PCI-E x16 mode, and not in the "cut-down" PCI-E x8 as it was implemented in the "classical" nForce 4 SLI. 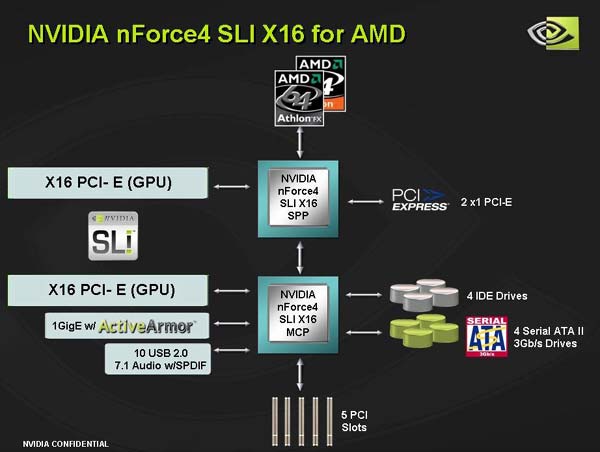 NVIDIA nForce 4 SLI 16x chipset That proved possible after reverting the chipset to the classical dual-bridge scheme made up of two north bridges: the already well-known МСР (functionally, it makes no difference from nForce4 Ultra), and its fairly "cut-down" SPP version that has only one PCI Express x16 channel and two PCI Express x1 channels. Important advantage of the new chipset is the possibility of more flexible differentiation among various options of nForce 4 for various market sectors. Developing this trend, NVIDIA is preparing also the integrated version of nForce 4 to be released by September, still known under the codename C51. As the graphic core, one of the versions of GeForce 6200 TurboCache will be used. VIAIn the previous years, the leading positioned on the market of chipsets for AMD processors were held by VIA. Even nowadays when its positions were seriously shattered under NVIDIA's pressing, VIA's market share is still large enough. Late last year, VIA announced the K8T890, its first chipset with the PCI Express interface for Athlon 64. However, that time the announcement proved "on paper", that is, the batch production of the new chipset did not start immediately. Moreover, the delay lasted for several months, and the mass supplies of motherboards based on K8T890 started only in summer this year. Unlike NVIDIA's "top-end" solutions, K8T890 is positioned by VIA as an inexpensive Mainstream solution that offers modern enough features. It differs from the predecessor, K8T800 Pro, in only the type of the graphic interface: the AGP8Х bus controller has been replaced with the PCI Express bus controller (20 independent lines). 16 of them fall on the graphic port PCI Express x16, with the remaining four reserved for an arbitrary use by motherboard manufacturers. 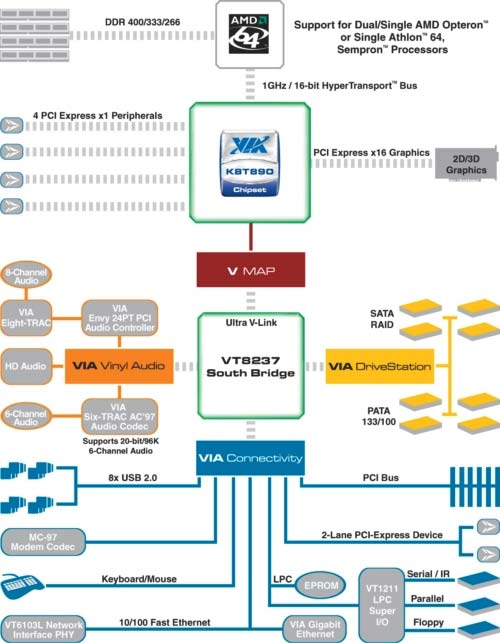 VIA K8T890 chipset While nForce4 is made up of one chip, K8T890 offers the classical dual-chip architecture. The VIA's chipset is made up of the north and south bridges which are linked by the proprietary Ultra V-Link bus of 1066 MB/s bandwidth. The north bridge of К8Т890 is connected to the CPU though a bi-directional HyperTransport bus (operating speed 1 GHz, bus bandwidth - 16 bit in each direction), and all the 20 channels of the PCI Express are also here. Therefore, the chipset's specifications in general could be regarded modern enough if it were not for the outdated south bridge VT8237R which is currently used to equip the К8Т890 and thus prevents it from competing on par versus nForce 4. For instance, the Serial ATA controller integrated in VIA VT8237R supports merely two SATA/150 ports versus four SATA/300 in nForce4 Ultra/SLI. Similar comparison could be also made regarding the network controllers of chipsets. NVIDIA nForce4 offers a Gigabit LAN controller with the hardware utility of network protection (ActiveArmor), whereas VIA's chipset is equipped with merely a primitive 10/100 Mbit/s LAN controller. Similar comparison can be made not in favor of VIA K8T890 even in the part of support for USB 2.0 ports. The VIA's chipset has merely eight of them, whereas NVIDIA nForce4 offers ten ports. As regards the integrated audio, VIA K8T890 that offers support for 8-channel AC97 audio is on par with nForce4. The long promised VT8251 has not only been represented so far, but it is still unknown when it will appear. In fact, despite the comparatively moderate functionality of VIA K8T890, the chipset can be in demand on the market. The thing is that this chipset is sold by the manufacturer cheaper than NVIDIA sells its nForce4, therefore, motherboards on the base of VIA's products cost much cheaper than those by its major competitor. An important advantage of K8T890 is the fact that it is quite suitable for thrifty overclockers since it is able providing a HyperTransport-independent cycling of PCI and PCI Express buses. Therefore, overclocking of Athlon 64 on motherboards built on VIA K8T890 can be done without any issues. A bit later, closer to the autumn of this year, the 890 series of chipsets should be complemented with one more representative - VIA K8T890 Pro in which the DualGFX Express technology will be implemented that provides a simultaneous operation of two graphic cards (by analogy with NVIDIA's SLI). The essence of DualGFX Express is in the possibility to configure 20 lines of PCI Express which are present in the north bridge, thus produce one full-featured PCI Express x16 slot and one PCI Express x4 slot which by its electrical performance will be compatible to PCI-E video cards. A good addition to the discreet chipset VIA K8T890/K8T890 Pro will be its integrated version - VIA K8M890 with the built-in video core DeltaChrome IGP which provides full support for DirectX 9. Closer to the end of 2005, one more novelty from VIA is expected - the K8T900 chipset in which the long-promised full support for SLI following the formula "PCI-E x8 + PCI-E x8" will be finally implemented. Officially, such a structure will be dubbed as DualGFX Express Pro. A companion of VIA K8T900 should be the rather belated south bridge VT8251 which will offer support for SerialATA/300, NCQ, RAID of level 5, additional PCI Express ports for peripherals and integrated 8-channel audio of HDA class. By now, we can tell for sure what will not definitely be there in VT8251: VIA believes that integration of a MAC-controller of Gigabit LAN into the chipset is not justified from both economical and functional viewpoints because one full-featured (MAC+PHY) external chip will cost cheaper and run (over the PCI-E х1 bus) not at all slower than the integrated. Next |
||||||||||||||
|
Management by AK Design VisualPharm.com |
|
|||




