MSI P7NGM (NVIDIA GeForce 9300)

Author:
Date: 25.12.2008 |
|
Recently, NVIDIA has represented a new series of integrated GeForce 9ххх chipsets aimed at the Intel platform. Release of this family occurred a bit later than the similar series for the AMD platform, which is explained by greater complexity of development. The thing is, chipsets for Intel processors offer an integrated memory controller. However, late in 2008 it should be specified that we mean LGA775 processors since processors of the new Nehalem architecture (LGA1366) offer an integrated memory controller (therefore, it is missing in the chipset).
Talking about the GeForce 9ххх series which includes GeForce 9300 and GeForce 9400 chipsets, we should point out a few important aspects. First, the chipset is of a single-chip make. Secondly, the chipsets are based on the G86 architecture, and the graphic core offers 16 shader processors. For comparison, the graphic core of NVIDIA GeForce 8200 (for the AMD platform) offers merely 8 similar processors. Thirdly, the only difference between GeForce 9300 and GeForce 9400 is in the clock speeds. In particular, the faster core of GeForce 9400 runs at 580 MHz, and the shader processors at 1.4 GHz. The core of GeForce 9300 is somehow slower: its frequency is 450 MHz, while the shader processors run at 1.2 GHz.
As it should be for the modern graphic core, chipsets of the GeForce 9ххх series support hardware decoding of video data in the H.264, VC1, and MPEG-2 formats. There is a dedicated NVIDIA PureVideo HD block responsible for that. Supported are also technologies like NVIDIA PhysX and CUDA.
As regards the expansion options, we should first note support for the PCI Express v2.0 bus whose total number of lanes is 20. That means the option of installing one (or even two) PEG slots for external video cards on the motherboard. Therefore, NVIDIA has implemented the HybridSLI technology which allows consolidating the computational resources of the external video card and the integrated video core. Besides, the engineers still have four vacant PCI-E lanes which can be used at own discretion (in particular, to plug in Gigabit LAN controllers).
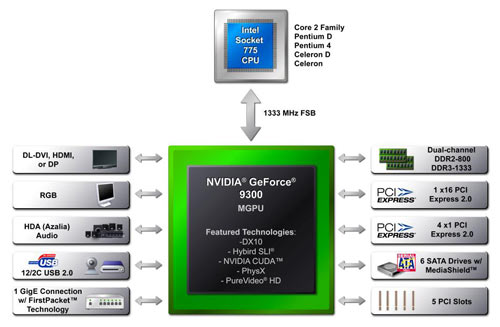
Besides the high-speed Ethernet, the new chipsets support six SerialATA II ports, 12 USB 2.0 ports, 7.1-channel LPCM HD Audio, as well as five PCI slots. The plugged in disks can be merged into a RAID array of levels 0, 1, 0+1, and 5. By the way, note that support for the ParallelATA is missing in the new chipsets. To implement it, the developers will have to install a separate controller. This is just the chip which is installed on MSI P7NGM which is the first representative of motherboards on the new series of NVIDIA chipsets that have been to our test lab.
MSI P7NGM Specifications
| MSI P7NGM |
| CPU |
- Intel Pentium 4 (Prescott (2M)/Gallatin/CedarMill) with the bus speeds 1066/800 MHz
- Dual-core Intel Pentium D / EE (Smithfield/Presler) with the bus speeds 1066/800 MHz
- Intel Celeron-D (Prescott/Conroe-L) with the bus speed 800 MHz
- Support for Intel Core 2 (Kentsfield (4 cores), Conroe (2 cores)) with the bus speeds 1333/1066/800 MHz
- Support for Intel Yorkfield, Wolfdale with the bus speeds 1333/1066/800 MHz
- Socket LGA775
- Support for HyperThreading |
| Chipset |
- NVIDIA GeForce 9300 |
| System memory |
- Two 240-pin slots for DDR2 SDRAM DIMM
- Maximum memory capacity 4 GB
- Supported memory DDR2 533/667/800
- Dual-channel memory access |
| Graphics |
- One PCI Express x16 slot
- Integrated graphic core GeForce 9300 |
| Expansion options |
- Two 32-bit PCI Bus Master slots
- One PCI Express x1 slot
- Eight USB 2.0 (4 integrated + 4 additional)
- Two IEEE1394 (Firewire; 1 integrated + 1 additional)
- LPCM High Definition Audio 7.1
- Gigabit Ethernet LAN controller |
| Overclocking options |
- FSB adjustable within 100 to 625 MHz in 1 MHz increments; multiplier adjustable
- Adjustable voltages on the CPU, memory, FSB, and the chipset
- MSI AiBooster |
| Disk subsystem |
- One link for UltraDMA133/100/66/33 Bus Master IDE (JMB368; with support for up to two ATAPI devices)
- Support for SerialATA II (6 links - GeForce 9300, with support for RAID) |
| BIOS |
- 4 Mbit Flash ROM
- AMI BIOS with support for Enhanced ACPI, DMI, Green, PnP Features |
| Misc |
- One port for FDD, two serial and one parallel ports, ports for PS/2 keyboard and mouse
- STR (Suspend to RAM)
- SPDIF Out |
| Power management |
- Wake-up on modem, mouse, keyboard, LAN, timer, and USB
- Main 24-pin ATX power connector
- Additional 4-pin power connector |
| Monitoring |
- Monitoring the temperature of the CPU, system, voltages, rotational speeds of the two fans
- Smart Fan |
| Dimensions |
- MicroATX form factor, 240x208 mm (9.6" x 8.2") |
Package
Package bundle
- motherboard;
- User's Manual in English;
- 2x CDs with software & drivers (for MS Windows XP and Vista);
- ParallelATA cable;
- one SerialATA cable;
- a cap for the rear panel of the housing.
The package bundle is quite scarce, but meets the level of a value product. For now, we can't tell anything else: we've got one of the first specimens of the board. In particular, there is not printed user's manual and you can't download the *.pdf version from the MSI's official web site because the description of the model is missing there.
MSI P7NGM: Layout and Features
The board's design has only one annoying trait - inconvenient positioning of the additional power connector.
Near the CPU socket, there is a 4-pin CPUFAN1 connector for a matching cooler.
Besides it, there is one 3-pin SYSFAN1 connector near the chipset. The connector does not have to be used because a mid-size radiator does quite a good job cooling the heat emission of the chipset:
Nearby, there is a couple of 240-pin DIMM slots for DDR2 memory modules, with the overall supported memory capacity being 4 GB.
Expansion options
The board uses a PCI Express x16 slot which is meant for video cards.
Besides it, MSI P7NGM uses two more "regular" PCI slots, as well as a PCI Express x1 slot. Due to the GeForce 9300 chipset, the board supports six SerialATA II ports with support for RAID arrays of the levels 0, 1, 0+1, 5.
We should also note that the chipset does not support the ParallelATA interface, but to implement it the engineers had to install an additional JMB368 controller. Another trait of the board is in that the chipset supports 12 USB2.0 ports. However, only 8 are implemented on the board: 4 on the rear panel, with 4 more plugged in with brackets (missing in the bundle). The board supports one more type of the serial bus. These are two FireWire ports which are implemented due to the additional JMB 381 chip (one on the rear panel, the other - via a bracket).
MSI P7NGM offers integrated 8-channel High Definition Audio, with the RealTek ALC888 chip used as the codec. Now a few words on the network support: the board uses a high-speed RTL 8111C (Gigabit Ethernet) LAN controller connected to the PCI Express (x1) bus.
The board's rear panel has the following configuration:
As compared to modern integrated boards, the rear panel of MSI P7NGM is archaic: there is neither DVI nor HDMI connector. On the other hand, the user gets a kit of outdated LPT and COM ports. By the way, the motherboard supports the second COM-port with a matching bracket.
Now on to the BIOS settings.
 |
Content: |
 |
|
 |
Top Stories: |
 |
 |
 |
MoBo:


|
 |
 |
 |
VGA Card:


|
 |
 |
 |
CPU & Memory:

|
|
|
