NVIDIA nForce 700i Series: new chipsets for the Intel platform

Author:
Date: 26.12.2007 |
|
We are introducing our readers to the functional capabilities of the new NVIDIA's recently announced family of nForce 700i chipsets for the Intel platform. You will see that the recent announcement of the new NVIDIA 3-Way SLI technology for the AMD platform was merely a "spice" before this announcement.
 For now, we can't yet present the test results for platforms built on the new chipsets since the samples have not yet arrived at our lab. However, we would recommend that you look into the "theoretical" details of NVIDIA nForce 700i chipsets. It's really worth it, because this time it's not a mere upgrade of the existing technologies, and, along with the details of NVIDIA 3-Way SLI implementation for the Intel platform, you'll be able to know much interesting about other innovations as well – for instance, the new Enthusiast System Architecture (ESA) technology and other absolutely new features for fine-tuning which allow attaining the maximum system performance. For now, we can't yet present the test results for platforms built on the new chipsets since the samples have not yet arrived at our lab. However, we would recommend that you look into the "theoretical" details of NVIDIA nForce 700i chipsets. It's really worth it, because this time it's not a mere upgrade of the existing technologies, and, along with the details of NVIDIA 3-Way SLI implementation for the Intel platform, you'll be able to know much interesting about other innovations as well – for instance, the new Enthusiast System Architecture (ESA) technology and other absolutely new features for fine-tuning which allow attaining the maximum system performance.
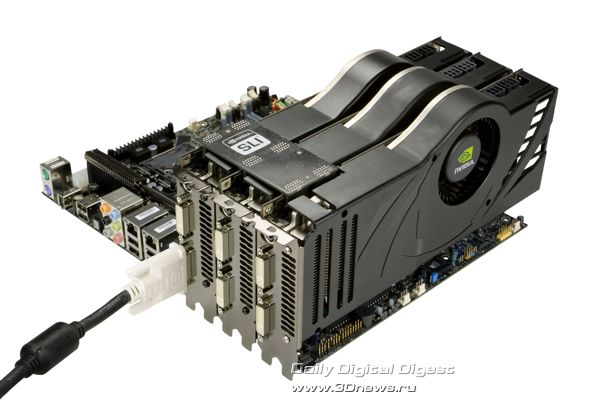 The NVIDIA nForce 700i family for the Intel platform currently includes two new MCP (Media and Communication processors) chips - nForce 780i SLI and nForce 750i SLI which are common in the certification for new 45-nm Intel processors with Yorkfield and Wolfdale cores; support for the PCI Express 2.0; full-featured support for DirectX 10 games in combination with GeForce video cards, including various NVIDIA SLI configurations. At the same time, new NVIDIA nForce 700i chipsets are essentially different from one another in the set of functional capabilities. These differences are well seen from the positioning of the chipsets: while nForce 780i SLI is aimed at building most powerful gaming systems that use the 3-Way SLI technology, the nForce 750i SLI is being positioned as a powerful solution with support for two video cards in the SLI mode, and a balanced price.
NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI MCP Chipset
The NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI chipset is the first platform solution to operate components certified within the ESA project (read on for details).
NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI supports 62 PCI Express buses, 32 of which being PCI Express 2.0, offers doubled performance as compared to the currently popular PCI Express 1.0 standard. In practice, this means attaining a peak performance in the PCIe 2.0 x16 configuration as high as 8 GB/s. NVIDIA nForce 780i allows configuring these 32 buses as 2?16, or 4?8, or 1?16, or 2?8. The remaining 30 PCI Express 1.0 buses can be configured as 1?16, 1?8, and 6?1.
NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI offers support for the 3-Way SLI mode, that is, operation of three video cards in the SLI mode using the special jumper - 3-Way SLI Connector.
In future, it is expected that the 3-Way SLI Connector mode, apart from the NVIDIA 3-Way SLI Connector board, may be implemented with three independent SLI connectors. Motherboards based on the nForce 780i and ready systems with support for the 3-way SLI will be equipped with such transient boards.
The current implementation of 3-way NVIDIA SLI mode is possible with the following video cards:
- NVIDIA GeForce 8800 GTX
- NVIDIA GeForce 8800 Ultra
According to NVIDIA, three NVIDIA GeForce 8800 GTX or GeForce 8800 Ultra in the 3-way NVIDIA SLI mode and HD screen resolution 2560x1600 provide a performance that is 2.8 times higher than the capabilities of systems with single video cards. Certainly, the NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI also supports the 2-way SLI mode as well as single-card operation.
At that, we must clarify the following important point:
Currently, the 3-way SLI mode is supported by systems powered by Windows Vista only, with installed NVIDIA ForceWare Windows Vista driver; this mode is not yet provided for Windows XP.
Among the reasons that finally brought the 3-way SLI technology to life, NVIDIA primarily mentions the possibility of its implementation with maximum available settings in modern games. For instance, none of the currently announced systems based on one or even two video cards is able to provide a comfortable gameplay in Crysis with the settings tuned to "high", while a system with the 3-way SLI with support for DirectX 10 is able providing a comfortable mode in Crysis with resolutions up to 1920 x 1200. Moreover, old games like Quake 4 can now be started with resolutions up to 2500 x 1600 and 8xAA, with the performance being as high as 150 fps. On the whole, the 3-way SLI mode is meant to provide sufficient performance with the XHD resolution and 60 fps in the 8xAA or 16xAA modes.
 While comparing the new 3-way SLI technology versus the Quad SLI based on 2-processor video cards GeForce 7900 GX2 or 7950 GX2 that was announced in mid-2006, NVIDIA points out that despite the high enough performance of the Quad SLI platform, there is a number of limitations for many high-end 3D games. In particular, the implementation of Quad SLI is much more demanding to the design of the PC housing, and the overall performance of such system will anyway be restricted by the capabilities of DirectX 9 which is not able to load all the four graphic processors efficiently. In this regard, the 3-way SLI technology appears to be more "user-friendly" because it allows for an additional upgrade whenever necessary and provides equally efficient operation for both DirectX 9 and DirectX 10, along with the compatibility to a wider list of games.
The 3-way SLI mode is enabled with the NVIDIA Control Panel utility in which you should set the SLI mode in the 3D Settings tab.
The activity of NVIDIA Control Panel can be monitored in the 3D Settings menu through setting the Show SLI Visual Indicators option, whereas the SLI x3 text is displayed on full-screen 3D applications (in what follows - SLI Visual Indicator in 3DMark2006).
Systems built on the NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI chipset support the JEDEC-standardized DDR2 memory, including that with EPP (Enhanced Performance Profiles), with clock speeds up to 1200 MHz, and the NV BIOS utility allows tuning the clock speeds and supply voltage within a wide range.
The nForce 780i chipset is made up of the three integrated circuits: nForce 780i SPP (NF780i-SLI), nForce 570 MCP (NF570I), and nForce 200 (NF200-SLI). The NVIDIA nForce 200 chip is a PCI Express-switch with one input and four output ports. The output ports in NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI MCP, in its turn, allow configuring two ?16 PCIe 2.0 or four x8 PCI Express 2.0 ports. Therefore, the interface between NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI SPP and NVIDIA nForce 200 provides the maximum bandwidth up to 4.5 GT/s per bus – more than enough to provide a full performance of graphic cards with the PCI Express 2.0 bus.
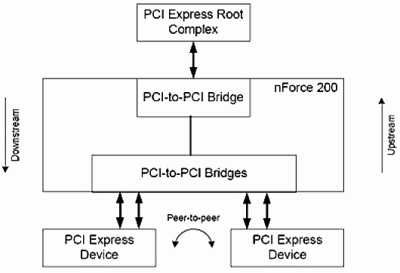 On the whole, the NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI MCP chipset offers a micro architecture that is similar to the interior of NVIDIA nForce 680i SLI MCP. The chipset is manufactured at the production capabilities of TSMC following the 90-nm process technology and supports all the modern Intel Socket 775 processors with the FSB up to 1333 MHz (and higher), including Intel Core 2 Extreme, Core 2 Quad, Core 2 Duo, Pentium, as well as the anticipated 45-nm chips of the Penryn family – the quad-core Yorkfield and dual-core Wolfdale. Along with that, NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI chipsets offer two integrated Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
Now, regarding the technologies and standards supported by the NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI.
NV BIOS - allows adjustment and monitoring of the latency timings, frequencies and supply voltages for most of the critical components of the motherboard. In accord with the requirements imposed by the latest Intel processors to motherboards, NV BIOS allows adjusting the CPU multiplier in 0.5 increments.
NV BIOS also offers the System Monitor utility which allows keeping track of the current power consumption readings, temperature modes of the CPU, the cooling system, and other key components of the system in real time.
Along with that, the NVIDIA Control Panel allows, using the NV BIOS, to provide a substantial "overclocking" of the system, and some motherboards can be overclocked over the bus to 1880 MHz.
NVIDIA Quicksync Technology - a technology that allows accelerating data exchange between the CPU and the memory, while the FSB and the memory interface are running in the Sync Mode.
FirstPacket Technology - allows the applications sensitive to latency timings, like VoIP as well as games, to distribute the limited resources just among those applications which first need that, while the other applications for which the latency is not so critical are switched to the so-called "slow line" mode.
DualNet Technology - allows arbitrarily configuring two Gigabit Ethernet ports integrated into the chipset - not only individually but also for attaining the maximum total performance.
Teaming - a technology that allows using both integrated LAN interfaces for joint operation as a single network connection. That is, we get some sort of 2 Gigabit Ethernet.
MediaShield Technology - a technology that allows for additional protection and gain in the data exchange while creating a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks). The MediaShield technology offers a special interface for configuring RAID arrays and control of their operation. Solutions based on NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI allow combining up to six SATA-2 hard disks into a single array; there are modes for switching six disks to the RAID 0 mode for maximum performance; three drives to the RAID 5 mode, and three remaining – to the RAID 0 array, and one more - to another RAID 5.
RoHS Compliance - all the integrated circuits in the NVIDIA nForce 780i SLI chipset are certified for the "green" RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive) standard and do not contain hazardous substances like lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybromide diphenyls, etc.
 |
Content: |
 |
|
 |
Top Stories: |
 |
 |
 |
MoBo:


|
 |
 |
 |
VGA Card:


|
 |
 |
 |
CPU & Memory:

|
|
|
